---
title: 如何升级
order: 3
---
相较于 v4,G6 v5 的新能力体现在:
- 🎞 **视觉与动画规范**,使用 JSON spec 或映射函数的方式定义样式与动画;
- 📂**信息分层**能力;
- 🎨 简单灵活的**主题**配置能力;
- 🤖 灵活强大的**数据处理**能力;
- 🎄 **树图**和**图**结构的融合;
- 🏀 **3D** 大图;
- 🚀 **性能**飞跃,包括渲染与布局计算;
- 🌠 **多渲染器**,可运行时切换;
- 📦 **包体积减少**,支持 TreeShaking。
还有其他一些微小而美好的改变:
- 轮廓包裹 Hull 支持文本配置;
- 折线支持自动避障;
- 文本自动适配宽度;
- 采用临时层画布提升交互性能;
- 图例自动从画布中获取样式。
正式版即将来袭。如果上面 Feature 是您所期待的,现在就可以使用 G6 5.0 Beta 版本进行尝鲜!若遇到任何升级问题,请在 GitHub 给我们留言。
为了支持上述全新能力,G6 5.0 相比于 v4 有比较大的 Breaking Change,这可能带来一定的升级成本。希望上面全新能力带来的收益远大于升级成本。
## 0️⃣. 新功能怎么用
参考 [如何使用新功能](./new-features.zh.md).
## 1️⃣. 数据格式变更
为了数据分层,防止数据污染,并更好地避免业务数据和渲染数据混杂的情况,和 v4 相比,v5 的数据结构有了比较大的变更,具体变更如下。G6 v5 提供了 v4 数据的转换处理器,可以在数据处理模块配置使用,例如:
```typescript
const graph = new Graph({
transforms: ['transform-v4-data'],
// ... 其他配置
data: v4data, // 一份 v4 格式的数据
});
```
v4 与 v5 的具体数据格式区别如下:
### v4 数据结构
```typescript
type GraphData = {
nodes: NodeModel[];
edges: EdgeModel[];
combos: ComboModel[];
};
type ItemModel = {
id: string;
type?: string; // 元素类型,e.g. 如是节点,则可能是 circle, rect 等注册过的节点类型名
label?: string; // label 的文本
color?: string; // keyShape 的颜色
size?: number | number[]; // keyShape 的大小
visible?: boolean;
style?: { [shapeAttr: string]: unkown }; // keyShape 的样式
labelCfg?: {
position?: string;
offset: number;
refX: number;
refY: number;
style?: { [shapeAttr: string]: unkown }; // label 的样式
background?: { [shapeAttr: string]: unkown }; // label 背景的样式
};
};
type NodeModel = ItemModel & {
comboId?: string;
x?: number;
y?: number;
anchorPoints?: number[][];
icon?: {
show?: boolean;
img?: string;
text?: string;
width?: number;
height?: number;
offset?: number;
};
linkPoints?: {
top?: boolean;
right?: boolean;
bottom?: boolean;
left?: boolean;
size?: number;
[shapeAttr: string]: unkown;
};
// 根据节点类型不同,有不同的图形相关配置,
// e.g. modelRect 的 preRect, image 的 clipCfg 等
};
type EdgeModel = ItemModel & {
source: string;
target: string;
sourceAnchor?: number;
targetAnchor?: number;
controlPoints?: IPoint[]; // polyline 特有
loopCfg?: LoopConfig; // loop 特有
curveOffset?: number | number[]; // quadratic/cubic 特有
minCurveOffset?: number | number[]; // quadratic/cubic 特有
curvePosition?: number | number[]; // quadratic/cubic 特有
};
```
### v5 数据结构
v5 的节点数据除了 id,边数据除了 id、source、target 这些字段外,所有的内容应当放到 data 对象中:
```typescript
// v5 用户输入数据格式
type GraphData = {
nodes: NodeModel[];
edges: EdgeModel[];
combos: ComboModel[];
};
type NodeModel = {
id: string;
data: {
type?: string; // 元素类型,e.g. 可能是 circle-node, rect-node
x?: number;
y?: number;
z?: number;
parentId?: string; // 父 combo 的 id
label?: string; // label 的文本
anchorPoints?: number[][];
badges?: {
type: 'icon' | 'text';
text: string;
position: BadgePosition;
}[];
icon?: {
type: 'icon' | 'text';
text?: string;
img?: string;
};
[key: string]: unknown; // 其他业务属性
};
};
type EdgeModel = {
id: string;
source: string;
target: string;
data: {
type?: string; // 元素类型,e.g. 可能是 line-edge
label?: string; // label 的文本
sourceAnchor?: number;
targetAnchor?: number;
icon?: {
type: 'icon' | 'text';
text?: string;
img?: string;
};
badge?: {
type: 'icon' | 'text';
text: string;
};
[key: string]: unknown; // 其他业务属性
};
};
```
## 2️⃣. 数据读取
### v4 数据读取
```typescript
import { Graph } from '@antv/g6';
import data from './data';
const graph = new Graph({
// ... 配置
});
graph.data(data);
graph.render();
// 或合并上面两行变为:graph.read(data);
```
### v5 数据读取
不再支持 `graph.data(data)` 和 `graph.render()`,仍然可以使用 `graph.read(data)`,或将数据直接配置到图上:
```typescript
import { Graph } from '@antv/g6';
import data from './data';
const graph = new Graph({
// ... 配置
data: data,
});
// 或使用:graph.read(data);
```
图配置中的 data 配置项类型 DataConfig 定义如下:
```typescript
export type DataConfig =
| GraphData
| InlineGraphDataConfig
| InlineTreeDataConfig
| FetchDataConfig;
export interface InlineGraphDataConfig {
type: 'graphData';
value: GraphData;
}
export interface InlineTreeDataConfig {
type: 'treeData';
value: TreeGraphData | TreeGraphData[];
}
export interface FetchDataConfig {
type: 'fetch';
value: string;
}
```
## 3️⃣. 树图
[图数据与树数据通用 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/feature/features/#treeAndGraph)
v5 新增树图相关 feature:
- 布局与 Graph 通用,Graph 可以指定根节点,使用最小生成树建立树结构后使用树图布局算法;
- 交互与 Graph 通用,Graph 也可以展开和收起“子树”了,即无回溯边的下游节点;
- 支持回溯边、环存在;
- 支持森林(多棵树)。
### v4 树图的问题
v4 树图有独立的数据结构(TreeGraphData 如下)、图类(TreeGraph)、交互(collapse-expand)、布局(Dendrogram/Indented/Mindmap/CompactBox)。数据结构、布局方法与 Graph 不通用。造成了用户在使用时的理解、转换困难:
- “怎么绘制多棵树?” - 不支持;
- “怎么在树图中增加边?” - 树图不允许存在环;
- “怎么在一般图中使用树图布局?- 布局不通用”。
5.0 将 TreeGraph 和 Graph 进行了全面合并。
```typescript
// TreeGraph
type TreeGraphData {
id: string;
[key: string]: unknown;
children: TreeGraphData[];
}
```
- TreeGraph 数据是嵌套的结构,不存在显式的边,父子关系为边;
- TreeGraph 不支持 combo 数据配置;
- 不支持环、森林(多棵树)。
### v5 树图
v5 的图支持了 TreeGraph 的数据格式,且原有树图和图的布局、交互都可以通用了。如果需要使用 TreeGraphData,只需要在配置 Graph 时给出一个数据类型的标记:
```typescript
const graph = new Graph({
// ... 其他配置项
data: {
type: 'treeData', // type 可以是 'graphData'、'treeData'、'fetch',其中 fetch 将在正式版支持
value: data, // value 在 type 是 treeData 时,可以是 TreeGraphData 或 TreeGraphData[] 以支持森林的绘制
},
});
```
在上面「数据读取」小节中介绍了 data 字段的类型,可以直接给 GraphData 类型的数据,那么 G6 将作为普通图处理,并在必要时(如使用树图布局、交互时)生成树图结构。也可以指定 type 为 'treeData' 后给 value 传入 TreeGraphData 类型的数据,那么 G6 将会存储树图结构,并转换为普通图数据进行存储。
也就是说,v5 中不再存在 TreeGraph Class,只有一个 Graph Class。那么 v4 中 TreeGraph Class 特有的 API 可以通过如下方式进行替代:
| 功能 | v4 TreeGraph API | v5 替代方案 |
| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| 在指定的父节点下添加子树 | treeGraph.addChild(data, parent) | graph.addData('node', { id: 'new-child', { parentId: 'parent-node-id' }}) |
| 删除指定的子树 | treeGraph.removeChild(id) | graph.removeData('node', 'id-of-a-node'),若移除的不是叶子节点,则其子节点升级为 roots |
| 差量更新子树 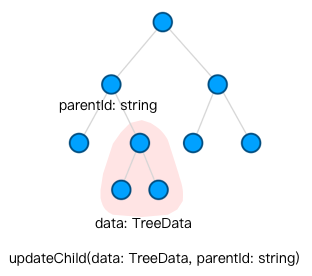 | treeGraph.updateChild(data, parentId) | graph.updateItem('node', { id: 'id-of-a-node', data: { ... }}) 分别更新每个节点。若需要新增一子节点,addData('node', { id: 'id-of-new-child', { parentId: 'parent-node-id' }}),需要注意顺序,先添加先继后添加后继 |
| 差量更新子树
| treeGraph.updateChild(data, parentId) | graph.updateItem('node', { id: 'id-of-a-node', data: { ... }}) 分别更新每个节点。若需要新增一子节点,addData('node', { id: 'id-of-new-child', { parentId: 'parent-node-id' }}),需要注意顺序,先添加先继后添加后继 |
| 差量更新子树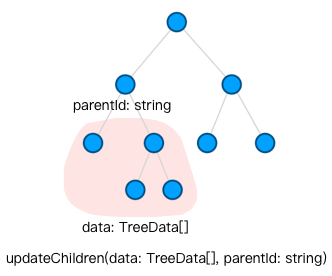 | treeGraph.updateChildren(data, parentId) | 同上 |
| 更改所属父节点 | 先从原父节点 removeChild,再在新父节点 addChild | graph.updateData('node', { id: 'child-id', { parentId: 'new-parent-id' }}) |
## 4️⃣. 元素类型名称
v4 中内置的节点类型有 circle、rect、ellipse、star、image 等。这些名称和图形的类型可能产生歧义。因此在 v5 中,将更名为 xx-node。例如 circle-node,rect-node,ellipse-node,star-node,image-node。
同理,边也将更名为 line-edge、polyline-edge、cubci-edge 等。
## 5️⃣. 功能引入
### v4 功能使用
v4 中所有功能都默认已经加入 G6,因此在 graph 配置时可以用字符串的方式指定,这导致了包体积庞大。例如:
```typescript
import { Graph } from '@antv/g6';
const graph = new Graph({
// ... 其他配置项
modes: {
default: ['drag-node', 'scroll-canvas'], // 交互名称
},
defaultNode: {
type: 'circle', // 节点类型名称
},
defaultEdge: {
type: 'rect', // 节点类型名称
},
layout: {
type: 'radial',
},
});
```
### v5 功能引入与使用
为了更好地支持 TreeShaking,v5 仅有部分最基础的能力会预先注册,其它已经实现的内置能力,但需要用户手动注册。同样地,自定义的能力也需要同样方式注册:
```typescript
import { Graph, extend, Extensions } from '@antv/g6';
// 外部引入的功能
import { ForceLayout as ForceLayoutWASM, supportsThreads, initThreads } from '@antv/layout-wasm';
// Class CustomBehaviorClass...
// Class CustomEdge...
const ExtGraph = extend(Graph, {
behaviors: {
'activate-relations': Extensions.ActivateRelations, // 内置的交互,未提前注册
'some-custom-behavior': CustomBehaviorClass, // 自定义交互
},
nodes: {
'modelRect-node': Extensions.ModelRectNode, // 内置的 modelRect 节点,未提前注册
},
edges: {
'custom-edge': CustomEdge, // 自定义边
},
layouts: {
'force-wasm': ForceLayoutWASM,
},
});
const supported = await supportsThreads();
const threads = await initThreads(supported);
// 使用 extend 后的图进行实例化
const graph = new ExtGraph({
// ... 其他配置项
modes: {
default: [
'drag-node', // 默认注册的交互
'activate-relations', // 刚刚引入并注册的内置交互
'some-custom-behavior', // 自定义并注册的交互
],
},
defaultNode: {
type: 'modelRect-node', // 刚刚引入并注册的内置节点类型
},
defaultEdge: {
type: 'custom-edge', // 自定义并注册的边类型
},
layout: {
type: 'force-wasm', // 刚刚从其他包引入并注册的布局算法
threads,
maxIteration: 200,
},
});
```
## 6️⃣. 布局使用
我们重构了 @antv/layout,考虑到包体积大小仅内置了 circular / concentric / grid / force 布局。在使用方式上和 v4 完全一致,通过 type 指定布局名称,传入其他布局参数:
```typescript
new Graph({
//...其他配置项
layout: {
type: 'force', // 布局名称
preventOverlap: true,
nodeSize: 30,
workerEnabled: true, // 支持在 WebWorker 中运行
},
});
```
对于非内置布局,我们提供了以下使用方式:
- @antv/layout 和 v4 保持一致的 JS 编写的串行布局算法;
- @antv/layout-wasm 提供基于 Rust 绑定到 WASM、多 WebWorker 并行的布局算法;
- @antv/layout-gpu 提供基于 WebGPU 的可并行布局算法;
- 用户完全自定义的布局。
相比 v4 多出了向 G6 运行时标准库注册布局这一步。另外,虽然由于实现不同有的需要额外的异步启动步骤,但是在 layout 的配置描述上均保持一致,即通过 type 指定布局名称,然后传入其他布局参数。
下面展示的是在 v5 中使用新增的 @antv/layout-wasm,首先需要向 G6 的运行时标准库注册,提供一个自定义布局名称,后续将它传给 `layout` 使用。
[WASM 布局 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/feature/features/#wasmLayouts)
```typescript
import { stdLib, Graph } from '@antv/g6';
import { supportsThreads, initThreads, ForceLayout as ForceLayoutWASM } from '@antv/layout-wasm';
// 注册自定义布局
const ExtGraph = extend(Graph, {
layouts: {
'force-wasm': ForceLayoutWASM,
},
});
// 启动 WebWorker 线程池
const supported = await supportsThreads();
const threads = await initThreads(supported);
// 使用扩展后的 Graph
new ExtGraph({
//... 省略其他配置
layout: {
type: 'force-wasm', // 与注册时命名一致
threads, // 线程配置
dimensions: 2,
maxIteration: 100,
//... 省略该布局的其他参数
},
});
```
如果我们提供的布局实现都无法满足需求,还可以完全自定义布局。在实现 @antv/layout 提供的 Layout 接口时,只需要实现 execute 方法,assign 置空即可,这样可以保证不影响原始的图模型数据。
```javascript
import { Layout, LayoutMapping } from '@antv/layout';
class MyCustomLayout implements Layout<{}> {
async assign(graph, options?: {}): Promise {
throw new Error('Method not implemented.');
}
async execute(graph, options?: {}): Promise {
const nodes = graph.getAllNodes();
return {
nodes: nodes.map((node) => ({
id: node.id,
data: {
x: 0,
y: 0,
},
})),
edges: [],
};
}
options: {};
id: 'myCustomLayout';
}
// 注册自定义布局
const ExtGraph = extend(Graph, {
layouts: {
myCustomLayout: MyCustomLayout,
},
});
// 使用扩展后的 Graph
new ExtGraph({
layout: {
type: 'myCustomLayout',
},
});
```
## 7️⃣. 节点/边/ combo 实例
G6 v4 向用户暴露了节点和边的 item 实例,但它们的大部分 API,Graph 都有覆盖。而我们更推荐使用 Graph 的 API,以方便多个相关节点和边之间的统一管理和联动。因此,我们在 v5 中不再暴露节点和边的 item,所以 API 收口在 Graph 上,可以通过 Graph 获得单个/多个节点/边的数据,但不能够得到 item。
### v4 使用 item 的情况
```typescript
// 获取图上所有元素实例
graph.getNodes();
graph.getEdges();
graph.getCombos();
// 监听中的元素对象
graph.on('node:click', (e) => {
const { item } = e; // item 即为被点击的元素实例
const itemType = item.getType(); // 获取元素类型
});
// 获得实例中的数据
item.getModel();
// 更新实例的数据
graph.updateItem(item, {
// 数据
});
// 增加节点/边/combo
graph.addItem('node', {
// ...数据
});
// 删除节点/边/combo
graph.removeItem(item);
```
### v5 替代 API
```typescript
// 获取图上所有元素的数据 (内部流转数据)
graph.getAllNodesData();
graph.getAllEdgesData();
graph.getAllCombosData();
// 监听
graph.on('node:click', (e) => {
// 被点击的元素类型,元素 id
const { itemType, itemId } = e;
});
// 获取单个元素数据 (内部流转数据)
graph.getNodeData(id);
graph.getEdgeData(id);
graph.getComboData(id);
// 更新单个/多个实例数据
graph.updateData('node', [nodeModel1, nodeModel2]);
// 增加单个/多个实例数据
graph.removeData('node', [nodeModel1, nodeModel2]);
// 删除单个/多个实例数据
graph.removeData('node', [id1, id2]);
```
## 8️⃣. 样式配置
v4 由于没有数据分层,详细的图形样式可以配置在数据中,也可以配置在 graph 的 defaultNode defaultEdge 配置项中。导致用户对数据的管理略有混乱。业务属性和样式配置可能混杂在一起。另外,v4 graph 的节点/边样式配置是静态的、全局的,不能根据不同数据做出不同的映射。
### v4 全局样式配置
```typescript
const graph = new Graph({
// ...其他配置
defaultNode: {
type: 'circle',
style: {
fill: '#f00',
r: 20,
},
},
defaultEdge: {
type: 'poliline',
style: {
stroke: '#0f0',
lineWidth: 2,
},
},
});
```
### v5 样式映射
在 v5 中我们更建议用户数据中仅保留必要的业务属性,以及重要的简单样式配置(例如文本内容、badges 内容等),把样式配置放在图的节点/边 mapper 中。Mapper 是 v5 将内部流转数据转换为渲染数据的映射器,由用户配置在 Graph JSON 配置中。当然,也有部分内置的 mapper 逻辑,用于将用户数据中的文本内容、badges 内容等转换到对应的图形属性上。
```typescript
const graph = new Graph({
// ...其他配置
node: nodeInnerModel => {
const { id, data } = nodeInnerModel;
// 返回值类型见下方 DisplayNodeModel 类型
return {
id,
data: {
...data,
keyShape: {
fill: data.important ? '#f00' : '#ccc',
r: 20
},
labelShape: {
text: data.label,
position: 'bottom'
},
}
}
},
// 边配置同理
edge: edgeInnerModel => {
// 返回值类型见下方 DisplayEdgeModel 类型
return {...}
}
});
// 样式配置返回的内容
type DisplayNodeModel = NodeModel & {
id: string;
type?: string; // 元素类型,e.g. 可能是 circle-node, rect-node
data: {
x?: number;
y?: number;
z?: number;
keyShape?: { [shapeAttr: string]: unkown }, // keyShape 的样式
// label 的配置和样式。未配置则无该图形
labelShape?: {
position?: string,
offsetX?: number,
offsetY?: number,
offsetZ?: number;
[shapeAttr: string]: unkown
},
labelBackground?: { [shapeAttr: string]: unkown }, // label 背景的样式。未配置则无该图形
iconShape?: { [shapeAttr: string]: unkown }, // icon 的样式。未配置则无该图形
badgeShapes?: {
// 所有 badge 图形的通用样式。未配置则无该图形
color?: string;
textColor?: string;
[shapeAttr: string]: unkown;
// 各个 badge 分别的样式和配置
[key: number]: {
position?: IBadgePosition;
color?: string;
textColor?: string;
[shapeAttr: string]: unkown;
};
};
anchorShapes?: {
// 所有 anchor 图形的通用样式。未配置则无该图形
color?: string;
textColor?: string;
size?: number;
offsetX?: number;
offsetY?: number;
offsetZ?: number;
[shapeAttr: string]: unkown;
// 各个 anchor 分别的样式和配置
[key: number]: {
position?: BadgePosition;
color?: string;
textColor?: string;
size?: number;
offsetX?: number;
offsetY?: number;
offsetZ?: number;
[shapeAttr: string]: unkown;
};
};
}
}
type DisplayEdgeModel = {
id: string;
source: string,
target: string,
data: {
type?: string, // 元素类型,e.g. 可能是 line-edge
sourceAnchor?: number,
targetAnchor?: number,
}
}
```
## 9️⃣. 事件与事件参数
v4 中 mousexx 事件,在 v5 中更改为 pointerxx 事件,能更好地兼容移动端事件,如下:
```typescript
// v4
graph.on('node:mousemove', (e) => {});
// v5
graph.on('node:pointermove', (e) => {});
// 其他类似事件名:
// mousemove -> pointermove
// mouseenter -> pointerenter
// mouseleave -> pointerleave
// mousedown -> pointerdown
// mouseup -> pointerup
```
### v4 事件参数
```typescript
type GraphEvent = {
item: Node | Edge | Combo;
target: Shape;
x: number;
y: number;
pointX: number;
pointY: number;
canvasX: number;
canvasY: number;
clientX: number;
clientY: number;
//... 其他
};
```
### v5 事件参数
v5 不再暴露元素,item 将不再存在于事件参数中,v5 事件参数如下:
```typescript
type GraphEvent = {
itemId: string | number;
itemType: 'node' | 'edge' | 'combo';
target: Shape;
// 四套坐标系下当前操作的坐标值
canvas: { x: number; y: number; z: number }; // 对应 v4 的 x y 或 pointerX pointerY,图形的绘制坐标
client: { x: number; y: number }; // 对应 v4 的 clientX clientY,相对于浏览器的坐标系
viewport: { x: number; y: number }; // 对应 v4 的 canvasX canvasY,相对于 Canvas DOM 的坐标系
screen: { x: number; y: number }; // 相对于整个屏幕的坐标系
//... 其他
};
```
## 🔟. 坐标系统
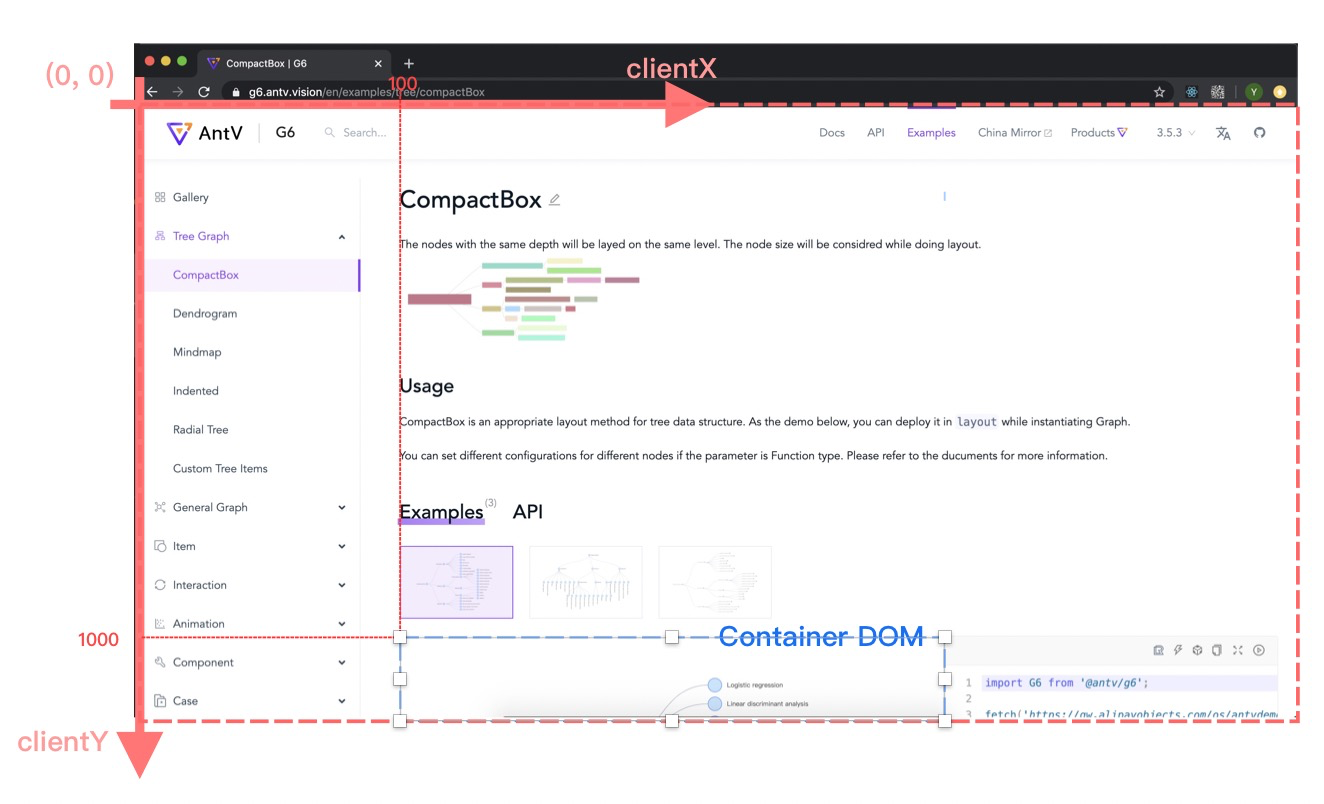
### v4 坐标系统
v4 的坐标系统(三套)见文档:https://g6.antv.antgroup.com/manual/advanced/coordinate-system
- v4 - clientX clientY
相对于浏览器的坐标系
| treeGraph.updateChildren(data, parentId) | 同上 |
| 更改所属父节点 | 先从原父节点 removeChild,再在新父节点 addChild | graph.updateData('node', { id: 'child-id', { parentId: 'new-parent-id' }}) |
## 4️⃣. 元素类型名称
v4 中内置的节点类型有 circle、rect、ellipse、star、image 等。这些名称和图形的类型可能产生歧义。因此在 v5 中,将更名为 xx-node。例如 circle-node,rect-node,ellipse-node,star-node,image-node。
同理,边也将更名为 line-edge、polyline-edge、cubci-edge 等。
## 5️⃣. 功能引入
### v4 功能使用
v4 中所有功能都默认已经加入 G6,因此在 graph 配置时可以用字符串的方式指定,这导致了包体积庞大。例如:
```typescript
import { Graph } from '@antv/g6';
const graph = new Graph({
// ... 其他配置项
modes: {
default: ['drag-node', 'scroll-canvas'], // 交互名称
},
defaultNode: {
type: 'circle', // 节点类型名称
},
defaultEdge: {
type: 'rect', // 节点类型名称
},
layout: {
type: 'radial',
},
});
```
### v5 功能引入与使用
为了更好地支持 TreeShaking,v5 仅有部分最基础的能力会预先注册,其它已经实现的内置能力,但需要用户手动注册。同样地,自定义的能力也需要同样方式注册:
```typescript
import { Graph, extend, Extensions } from '@antv/g6';
// 外部引入的功能
import { ForceLayout as ForceLayoutWASM, supportsThreads, initThreads } from '@antv/layout-wasm';
// Class CustomBehaviorClass...
// Class CustomEdge...
const ExtGraph = extend(Graph, {
behaviors: {
'activate-relations': Extensions.ActivateRelations, // 内置的交互,未提前注册
'some-custom-behavior': CustomBehaviorClass, // 自定义交互
},
nodes: {
'modelRect-node': Extensions.ModelRectNode, // 内置的 modelRect 节点,未提前注册
},
edges: {
'custom-edge': CustomEdge, // 自定义边
},
layouts: {
'force-wasm': ForceLayoutWASM,
},
});
const supported = await supportsThreads();
const threads = await initThreads(supported);
// 使用 extend 后的图进行实例化
const graph = new ExtGraph({
// ... 其他配置项
modes: {
default: [
'drag-node', // 默认注册的交互
'activate-relations', // 刚刚引入并注册的内置交互
'some-custom-behavior', // 自定义并注册的交互
],
},
defaultNode: {
type: 'modelRect-node', // 刚刚引入并注册的内置节点类型
},
defaultEdge: {
type: 'custom-edge', // 自定义并注册的边类型
},
layout: {
type: 'force-wasm', // 刚刚从其他包引入并注册的布局算法
threads,
maxIteration: 200,
},
});
```
## 6️⃣. 布局使用
我们重构了 @antv/layout,考虑到包体积大小仅内置了 circular / concentric / grid / force 布局。在使用方式上和 v4 完全一致,通过 type 指定布局名称,传入其他布局参数:
```typescript
new Graph({
//...其他配置项
layout: {
type: 'force', // 布局名称
preventOverlap: true,
nodeSize: 30,
workerEnabled: true, // 支持在 WebWorker 中运行
},
});
```
对于非内置布局,我们提供了以下使用方式:
- @antv/layout 和 v4 保持一致的 JS 编写的串行布局算法;
- @antv/layout-wasm 提供基于 Rust 绑定到 WASM、多 WebWorker 并行的布局算法;
- @antv/layout-gpu 提供基于 WebGPU 的可并行布局算法;
- 用户完全自定义的布局。
相比 v4 多出了向 G6 运行时标准库注册布局这一步。另外,虽然由于实现不同有的需要额外的异步启动步骤,但是在 layout 的配置描述上均保持一致,即通过 type 指定布局名称,然后传入其他布局参数。
下面展示的是在 v5 中使用新增的 @antv/layout-wasm,首先需要向 G6 的运行时标准库注册,提供一个自定义布局名称,后续将它传给 `layout` 使用。
[WASM 布局 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/feature/features/#wasmLayouts)
```typescript
import { stdLib, Graph } from '@antv/g6';
import { supportsThreads, initThreads, ForceLayout as ForceLayoutWASM } from '@antv/layout-wasm';
// 注册自定义布局
const ExtGraph = extend(Graph, {
layouts: {
'force-wasm': ForceLayoutWASM,
},
});
// 启动 WebWorker 线程池
const supported = await supportsThreads();
const threads = await initThreads(supported);
// 使用扩展后的 Graph
new ExtGraph({
//... 省略其他配置
layout: {
type: 'force-wasm', // 与注册时命名一致
threads, // 线程配置
dimensions: 2,
maxIteration: 100,
//... 省略该布局的其他参数
},
});
```
如果我们提供的布局实现都无法满足需求,还可以完全自定义布局。在实现 @antv/layout 提供的 Layout 接口时,只需要实现 execute 方法,assign 置空即可,这样可以保证不影响原始的图模型数据。
```javascript
import { Layout, LayoutMapping } from '@antv/layout';
class MyCustomLayout implements Layout<{}> {
async assign(graph, options?: {}): Promise {
throw new Error('Method not implemented.');
}
async execute(graph, options?: {}): Promise {
const nodes = graph.getAllNodes();
return {
nodes: nodes.map((node) => ({
id: node.id,
data: {
x: 0,
y: 0,
},
})),
edges: [],
};
}
options: {};
id: 'myCustomLayout';
}
// 注册自定义布局
const ExtGraph = extend(Graph, {
layouts: {
myCustomLayout: MyCustomLayout,
},
});
// 使用扩展后的 Graph
new ExtGraph({
layout: {
type: 'myCustomLayout',
},
});
```
## 7️⃣. 节点/边/ combo 实例
G6 v4 向用户暴露了节点和边的 item 实例,但它们的大部分 API,Graph 都有覆盖。而我们更推荐使用 Graph 的 API,以方便多个相关节点和边之间的统一管理和联动。因此,我们在 v5 中不再暴露节点和边的 item,所以 API 收口在 Graph 上,可以通过 Graph 获得单个/多个节点/边的数据,但不能够得到 item。
### v4 使用 item 的情况
```typescript
// 获取图上所有元素实例
graph.getNodes();
graph.getEdges();
graph.getCombos();
// 监听中的元素对象
graph.on('node:click', (e) => {
const { item } = e; // item 即为被点击的元素实例
const itemType = item.getType(); // 获取元素类型
});
// 获得实例中的数据
item.getModel();
// 更新实例的数据
graph.updateItem(item, {
// 数据
});
// 增加节点/边/combo
graph.addItem('node', {
// ...数据
});
// 删除节点/边/combo
graph.removeItem(item);
```
### v5 替代 API
```typescript
// 获取图上所有元素的数据 (内部流转数据)
graph.getAllNodesData();
graph.getAllEdgesData();
graph.getAllCombosData();
// 监听
graph.on('node:click', (e) => {
// 被点击的元素类型,元素 id
const { itemType, itemId } = e;
});
// 获取单个元素数据 (内部流转数据)
graph.getNodeData(id);
graph.getEdgeData(id);
graph.getComboData(id);
// 更新单个/多个实例数据
graph.updateData('node', [nodeModel1, nodeModel2]);
// 增加单个/多个实例数据
graph.removeData('node', [nodeModel1, nodeModel2]);
// 删除单个/多个实例数据
graph.removeData('node', [id1, id2]);
```
## 8️⃣. 样式配置
v4 由于没有数据分层,详细的图形样式可以配置在数据中,也可以配置在 graph 的 defaultNode defaultEdge 配置项中。导致用户对数据的管理略有混乱。业务属性和样式配置可能混杂在一起。另外,v4 graph 的节点/边样式配置是静态的、全局的,不能根据不同数据做出不同的映射。
### v4 全局样式配置
```typescript
const graph = new Graph({
// ...其他配置
defaultNode: {
type: 'circle',
style: {
fill: '#f00',
r: 20,
},
},
defaultEdge: {
type: 'poliline',
style: {
stroke: '#0f0',
lineWidth: 2,
},
},
});
```
### v5 样式映射
在 v5 中我们更建议用户数据中仅保留必要的业务属性,以及重要的简单样式配置(例如文本内容、badges 内容等),把样式配置放在图的节点/边 mapper 中。Mapper 是 v5 将内部流转数据转换为渲染数据的映射器,由用户配置在 Graph JSON 配置中。当然,也有部分内置的 mapper 逻辑,用于将用户数据中的文本内容、badges 内容等转换到对应的图形属性上。
```typescript
const graph = new Graph({
// ...其他配置
node: nodeInnerModel => {
const { id, data } = nodeInnerModel;
// 返回值类型见下方 DisplayNodeModel 类型
return {
id,
data: {
...data,
keyShape: {
fill: data.important ? '#f00' : '#ccc',
r: 20
},
labelShape: {
text: data.label,
position: 'bottom'
},
}
}
},
// 边配置同理
edge: edgeInnerModel => {
// 返回值类型见下方 DisplayEdgeModel 类型
return {...}
}
});
// 样式配置返回的内容
type DisplayNodeModel = NodeModel & {
id: string;
type?: string; // 元素类型,e.g. 可能是 circle-node, rect-node
data: {
x?: number;
y?: number;
z?: number;
keyShape?: { [shapeAttr: string]: unkown }, // keyShape 的样式
// label 的配置和样式。未配置则无该图形
labelShape?: {
position?: string,
offsetX?: number,
offsetY?: number,
offsetZ?: number;
[shapeAttr: string]: unkown
},
labelBackground?: { [shapeAttr: string]: unkown }, // label 背景的样式。未配置则无该图形
iconShape?: { [shapeAttr: string]: unkown }, // icon 的样式。未配置则无该图形
badgeShapes?: {
// 所有 badge 图形的通用样式。未配置则无该图形
color?: string;
textColor?: string;
[shapeAttr: string]: unkown;
// 各个 badge 分别的样式和配置
[key: number]: {
position?: IBadgePosition;
color?: string;
textColor?: string;
[shapeAttr: string]: unkown;
};
};
anchorShapes?: {
// 所有 anchor 图形的通用样式。未配置则无该图形
color?: string;
textColor?: string;
size?: number;
offsetX?: number;
offsetY?: number;
offsetZ?: number;
[shapeAttr: string]: unkown;
// 各个 anchor 分别的样式和配置
[key: number]: {
position?: BadgePosition;
color?: string;
textColor?: string;
size?: number;
offsetX?: number;
offsetY?: number;
offsetZ?: number;
[shapeAttr: string]: unkown;
};
};
}
}
type DisplayEdgeModel = {
id: string;
source: string,
target: string,
data: {
type?: string, // 元素类型,e.g. 可能是 line-edge
sourceAnchor?: number,
targetAnchor?: number,
}
}
```
## 9️⃣. 事件与事件参数
v4 中 mousexx 事件,在 v5 中更改为 pointerxx 事件,能更好地兼容移动端事件,如下:
```typescript
// v4
graph.on('node:mousemove', (e) => {});
// v5
graph.on('node:pointermove', (e) => {});
// 其他类似事件名:
// mousemove -> pointermove
// mouseenter -> pointerenter
// mouseleave -> pointerleave
// mousedown -> pointerdown
// mouseup -> pointerup
```
### v4 事件参数
```typescript
type GraphEvent = {
item: Node | Edge | Combo;
target: Shape;
x: number;
y: number;
pointX: number;
pointY: number;
canvasX: number;
canvasY: number;
clientX: number;
clientY: number;
//... 其他
};
```
### v5 事件参数
v5 不再暴露元素,item 将不再存在于事件参数中,v5 事件参数如下:
```typescript
type GraphEvent = {
itemId: string | number;
itemType: 'node' | 'edge' | 'combo';
target: Shape;
// 四套坐标系下当前操作的坐标值
canvas: { x: number; y: number; z: number }; // 对应 v4 的 x y 或 pointerX pointerY,图形的绘制坐标
client: { x: number; y: number }; // 对应 v4 的 clientX clientY,相对于浏览器的坐标系
viewport: { x: number; y: number }; // 对应 v4 的 canvasX canvasY,相对于 Canvas DOM 的坐标系
screen: { x: number; y: number }; // 相对于整个屏幕的坐标系
//... 其他
};
```
## 🔟. 坐标系统
### v4 坐标系统
v4 的坐标系统(三套)见文档:https://g6.antv.antgroup.com/manual/advanced/coordinate-system
- v4 - clientX clientY
相对于浏览器的坐标系
 - v4 - canvasX canvasY
相对于 canvas DOM 的坐标系
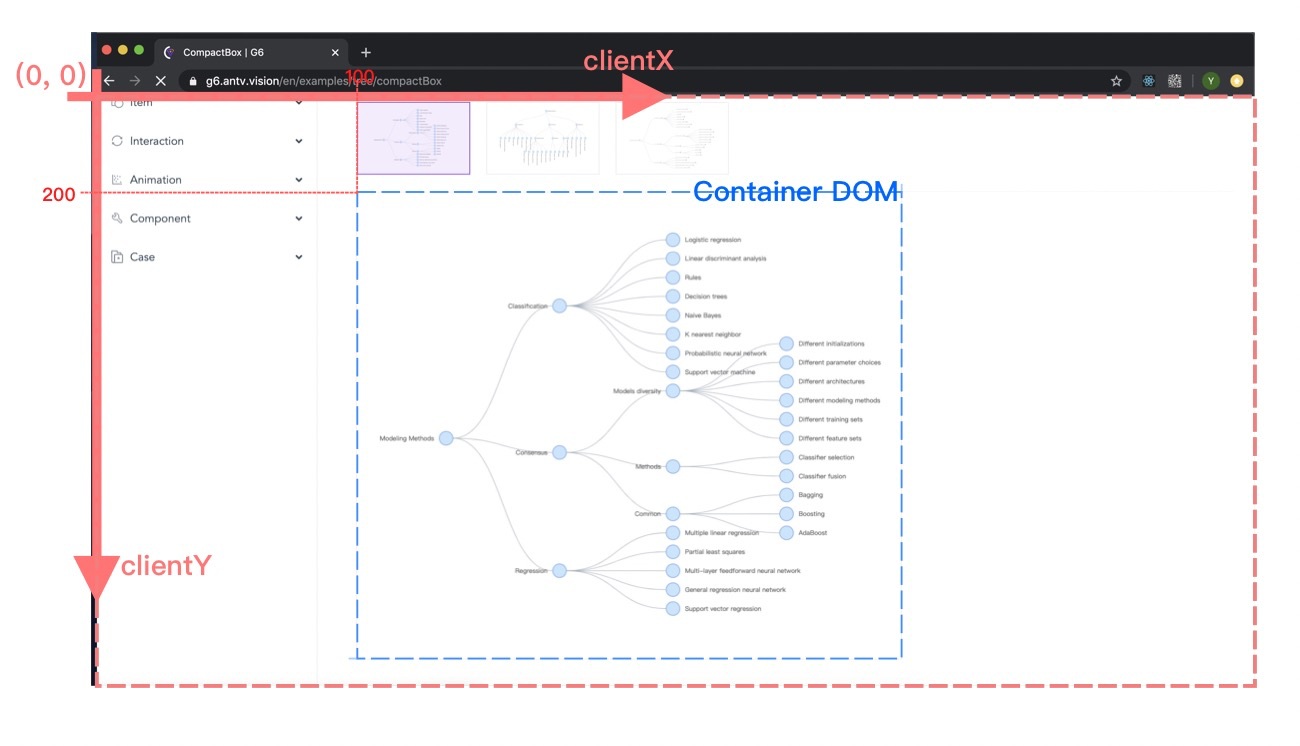
- v4 - canvasX canvasY
相对于 canvas DOM 的坐标系
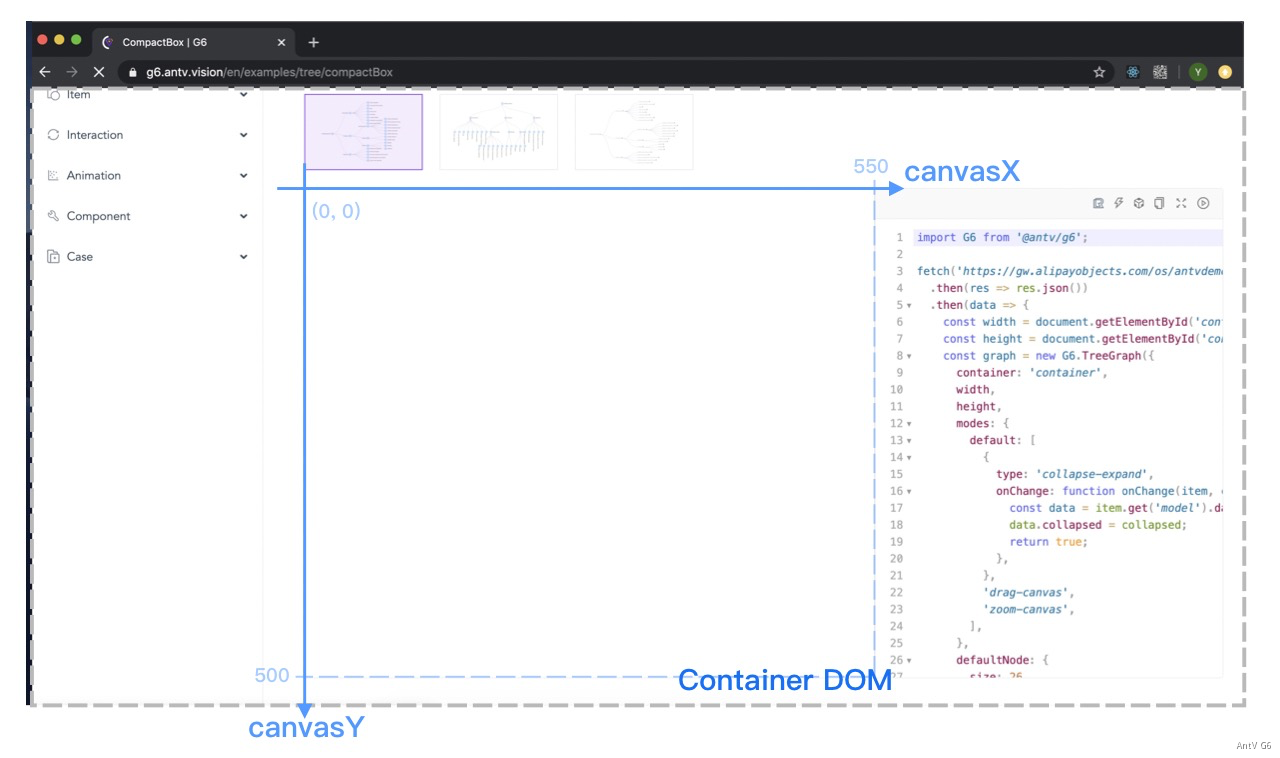 - v4 - pointX pointY (= v4 事件中的 x y)
图形绘制坐标系
- v4 - pointX pointY (= v4 事件中的 x y)
图形绘制坐标系
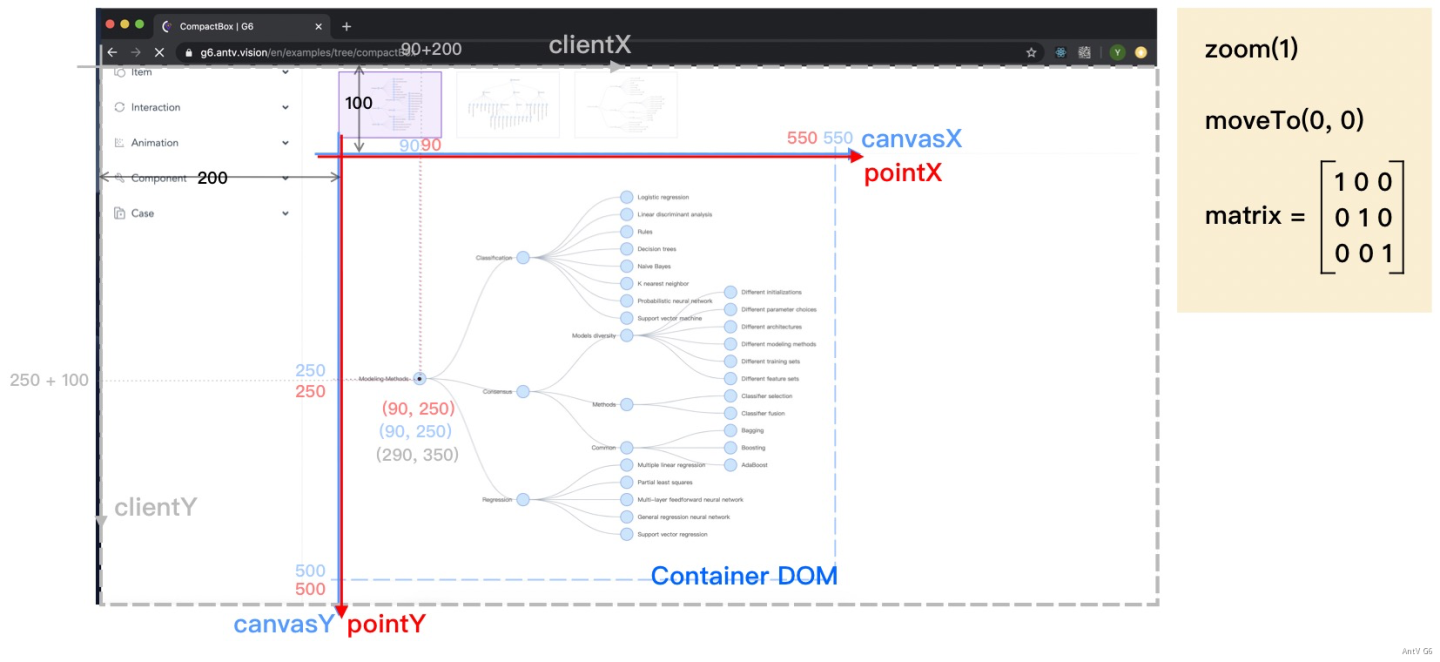 ### v5 坐标系
需要注意的是,v5 中的坐标系(四套)命名有所不同。
| 含义 | v4 坐标名 | v5 坐标名 |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------- |
| 图形的绘制坐标 | { x, y } 或 { pointerX, pointerY } | canvas: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
| 相对于浏览器的坐标系 | { clientX, clientY } | client: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
| 相对于 Canvas DOM 的坐标系 | { canvasX, canvasY } | viewport: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
| 相对于整个屏幕的坐标系
### v5 坐标系
需要注意的是,v5 中的坐标系(四套)命名有所不同。
| 含义 | v4 坐标名 | v5 坐标名 |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------- |
| 图形的绘制坐标 | { x, y } 或 { pointerX, pointerY } | canvas: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
| 相对于浏览器的坐标系 | { clientX, clientY } | client: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
| 相对于 Canvas DOM 的坐标系 | { canvasX, canvasY } | viewport: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
| 相对于整个屏幕的坐标系 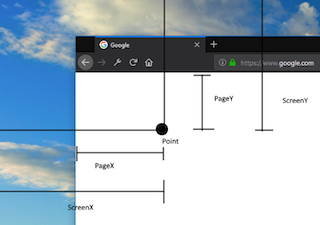 | 无 | screen: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
## 🌸. 其他微小而美好的改变
- 轮廓包裹 Hull 支持文本配置:
只需要为 Hull 实例配置 labelShape 即可,可以指定其相对位置(`position`)在 hull 的上、下、左、右四个方向。
[Hull 支持文本 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/interaction/hull/#hull)
| 无 | screen: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
## 🌸. 其他微小而美好的改变
- 轮廓包裹 Hull 支持文本配置:
只需要为 Hull 实例配置 labelShape 即可,可以指定其相对位置(`position`)在 hull 的上、下、左、右四个方向。
[Hull 支持文本 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/interaction/hull/#hull)
 - 折线支持自动避障:
设置边的 `keyShape.routeCfg.obstacleAvoidance: true` 即可自动躲避节点。
[Polyline 避障 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/item/defaultEdges/#polyline3)
- 折线支持自动避障:
设置边的 `keyShape.routeCfg.obstacleAvoidance: true` 即可自动躲避节点。
[Polyline 避障 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/item/defaultEdges/#polyline3)
 - 文本自动适配宽度:
设置节点文本图形的 `maxWidth`,可以为数字代表允许的最大宽度的像素值,也可以是百分比字符串代表占 keyShape 的比例。例如:
```javascript
const graph = new Graph({
node: {
labelShape: {
maxWidth: '120%',
},
},
});
```
[文本自适应 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/item/label/#copyLabel)
- 文本自动适配宽度:
设置节点文本图形的 `maxWidth`,可以为数字代表允许的最大宽度的像素值,也可以是百分比字符串代表占 keyShape 的比例。例如:
```javascript
const graph = new Graph({
node: {
labelShape: {
maxWidth: '120%',
},
},
});
```
[文本自适应 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/item/label/#copyLabel)
 - 采用临时层画布提升交互性能:
- 采用临时层画布提升交互性能:
 - 图例自动从画布中获取样式:
- 图例自动从画布中获取样式:


 - v4 - canvasX canvasY
相对于 canvas DOM 的坐标系
- v4 - canvasX canvasY
相对于 canvas DOM 的坐标系
 - v4 - pointX pointY (= v4 事件中的 x y)
图形绘制坐标系
- v4 - pointX pointY (= v4 事件中的 x y)
图形绘制坐标系
 ### v5 坐标系
需要注意的是,v5 中的坐标系(四套)命名有所不同。
| 含义 | v4 坐标名 | v5 坐标名 |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------- |
| 图形的绘制坐标 | { x, y } 或 { pointerX, pointerY } | canvas: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
| 相对于浏览器的坐标系 | { clientX, clientY } | client: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
| 相对于 Canvas DOM 的坐标系 | { canvasX, canvasY } | viewport: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
| 相对于整个屏幕的坐标系
### v5 坐标系
需要注意的是,v5 中的坐标系(四套)命名有所不同。
| 含义 | v4 坐标名 | v5 坐标名 |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------- |
| 图形的绘制坐标 | { x, y } 或 { pointerX, pointerY } | canvas: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
| 相对于浏览器的坐标系 | { clientX, clientY } | client: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
| 相对于 Canvas DOM 的坐标系 | { canvasX, canvasY } | viewport: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
| 相对于整个屏幕的坐标系  | 无 | screen: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
## 🌸. 其他微小而美好的改变
- 轮廓包裹 Hull 支持文本配置:
只需要为 Hull 实例配置 labelShape 即可,可以指定其相对位置(`position`)在 hull 的上、下、左、右四个方向。
[Hull 支持文本 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/interaction/hull/#hull)
| 无 | screen: { x: number; y: number; z: number } |
## 🌸. 其他微小而美好的改变
- 轮廓包裹 Hull 支持文本配置:
只需要为 Hull 实例配置 labelShape 即可,可以指定其相对位置(`position`)在 hull 的上、下、左、右四个方向。
[Hull 支持文本 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/interaction/hull/#hull)
 - 折线支持自动避障:
设置边的 `keyShape.routeCfg.obstacleAvoidance: true` 即可自动躲避节点。
[Polyline 避障 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/item/defaultEdges/#polyline3)
- 折线支持自动避障:
设置边的 `keyShape.routeCfg.obstacleAvoidance: true` 即可自动躲避节点。
[Polyline 避障 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/item/defaultEdges/#polyline3)
 - 文本自动适配宽度:
设置节点文本图形的 `maxWidth`,可以为数字代表允许的最大宽度的像素值,也可以是百分比字符串代表占 keyShape 的比例。例如:
```javascript
const graph = new Graph({
node: {
labelShape: {
maxWidth: '120%',
},
},
});
```
[文本自适应 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/item/label/#copyLabel)
- 文本自动适配宽度:
设置节点文本图形的 `maxWidth`,可以为数字代表允许的最大宽度的像素值,也可以是百分比字符串代表占 keyShape 的比例。例如:
```javascript
const graph = new Graph({
node: {
labelShape: {
maxWidth: '120%',
},
},
});
```
[文本自适应 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/item/label/#copyLabel)
 - 采用临时层画布提升交互性能:
- 采用临时层画布提升交互性能:
 - 图例自动从画布中获取样式:
- 图例自动从画布中获取样式:

 | treeGraph.updateChild(data, parentId) | graph.updateItem('node', { id: 'id-of-a-node', data: { ... }}) 分别更新每个节点。若需要新增一子节点,addData('node', { id: 'id-of-new-child', { parentId: 'parent-node-id' }}),需要注意顺序,先添加先继后添加后继 |
| 差量更新子树
| treeGraph.updateChild(data, parentId) | graph.updateItem('node', { id: 'id-of-a-node', data: { ... }}) 分别更新每个节点。若需要新增一子节点,addData('node', { id: 'id-of-new-child', { parentId: 'parent-node-id' }}),需要注意顺序,先添加先继后添加后继 |
| 差量更新子树 | treeGraph.updateChildren(data, parentId) | 同上 |
| 更改所属父节点 | 先从原父节点 removeChild,再在新父节点 addChild | graph.updateData('node', { id: 'child-id', { parentId: 'new-parent-id' }}) |
## 4️⃣. 元素类型名称
v4 中内置的节点类型有 circle、rect、ellipse、star、image 等。这些名称和图形的类型可能产生歧义。因此在 v5 中,将更名为 xx-node。例如 circle-node,rect-node,ellipse-node,star-node,image-node。
同理,边也将更名为 line-edge、polyline-edge、cubci-edge 等。
## 5️⃣. 功能引入
### v4 功能使用
v4 中所有功能都默认已经加入 G6,因此在 graph 配置时可以用字符串的方式指定,这导致了包体积庞大。例如:
```typescript
import { Graph } from '@antv/g6';
const graph = new Graph({
// ... 其他配置项
modes: {
default: ['drag-node', 'scroll-canvas'], // 交互名称
},
defaultNode: {
type: 'circle', // 节点类型名称
},
defaultEdge: {
type: 'rect', // 节点类型名称
},
layout: {
type: 'radial',
},
});
```
### v5 功能引入与使用
为了更好地支持 TreeShaking,v5 仅有部分最基础的能力会预先注册,其它已经实现的内置能力,但需要用户手动注册。同样地,自定义的能力也需要同样方式注册:
```typescript
import { Graph, extend, Extensions } from '@antv/g6';
// 外部引入的功能
import { ForceLayout as ForceLayoutWASM, supportsThreads, initThreads } from '@antv/layout-wasm';
// Class CustomBehaviorClass...
// Class CustomEdge...
const ExtGraph = extend(Graph, {
behaviors: {
'activate-relations': Extensions.ActivateRelations, // 内置的交互,未提前注册
'some-custom-behavior': CustomBehaviorClass, // 自定义交互
},
nodes: {
'modelRect-node': Extensions.ModelRectNode, // 内置的 modelRect 节点,未提前注册
},
edges: {
'custom-edge': CustomEdge, // 自定义边
},
layouts: {
'force-wasm': ForceLayoutWASM,
},
});
const supported = await supportsThreads();
const threads = await initThreads(supported);
// 使用 extend 后的图进行实例化
const graph = new ExtGraph({
// ... 其他配置项
modes: {
default: [
'drag-node', // 默认注册的交互
'activate-relations', // 刚刚引入并注册的内置交互
'some-custom-behavior', // 自定义并注册的交互
],
},
defaultNode: {
type: 'modelRect-node', // 刚刚引入并注册的内置节点类型
},
defaultEdge: {
type: 'custom-edge', // 自定义并注册的边类型
},
layout: {
type: 'force-wasm', // 刚刚从其他包引入并注册的布局算法
threads,
maxIteration: 200,
},
});
```
## 6️⃣. 布局使用
我们重构了 @antv/layout,考虑到包体积大小仅内置了 circular / concentric / grid / force 布局。在使用方式上和 v4 完全一致,通过 type 指定布局名称,传入其他布局参数:
```typescript
new Graph({
//...其他配置项
layout: {
type: 'force', // 布局名称
preventOverlap: true,
nodeSize: 30,
workerEnabled: true, // 支持在 WebWorker 中运行
},
});
```
对于非内置布局,我们提供了以下使用方式:
- @antv/layout 和 v4 保持一致的 JS 编写的串行布局算法;
- @antv/layout-wasm 提供基于 Rust 绑定到 WASM、多 WebWorker 并行的布局算法;
- @antv/layout-gpu 提供基于 WebGPU 的可并行布局算法;
- 用户完全自定义的布局。
相比 v4 多出了向 G6 运行时标准库注册布局这一步。另外,虽然由于实现不同有的需要额外的异步启动步骤,但是在 layout 的配置描述上均保持一致,即通过 type 指定布局名称,然后传入其他布局参数。
下面展示的是在 v5 中使用新增的 @antv/layout-wasm,首先需要向 G6 的运行时标准库注册,提供一个自定义布局名称,后续将它传给 `layout` 使用。
[WASM 布局 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/feature/features/#wasmLayouts)
```typescript
import { stdLib, Graph } from '@antv/g6';
import { supportsThreads, initThreads, ForceLayout as ForceLayoutWASM } from '@antv/layout-wasm';
// 注册自定义布局
const ExtGraph = extend(Graph, {
layouts: {
'force-wasm': ForceLayoutWASM,
},
});
// 启动 WebWorker 线程池
const supported = await supportsThreads();
const threads = await initThreads(supported);
// 使用扩展后的 Graph
new ExtGraph({
//... 省略其他配置
layout: {
type: 'force-wasm', // 与注册时命名一致
threads, // 线程配置
dimensions: 2,
maxIteration: 100,
//... 省略该布局的其他参数
},
});
```
如果我们提供的布局实现都无法满足需求,还可以完全自定义布局。在实现 @antv/layout 提供的 Layout 接口时,只需要实现 execute 方法,assign 置空即可,这样可以保证不影响原始的图模型数据。
```javascript
import { Layout, LayoutMapping } from '@antv/layout';
class MyCustomLayout implements Layout<{}> {
async assign(graph, options?: {}): Promise
| treeGraph.updateChildren(data, parentId) | 同上 |
| 更改所属父节点 | 先从原父节点 removeChild,再在新父节点 addChild | graph.updateData('node', { id: 'child-id', { parentId: 'new-parent-id' }}) |
## 4️⃣. 元素类型名称
v4 中内置的节点类型有 circle、rect、ellipse、star、image 等。这些名称和图形的类型可能产生歧义。因此在 v5 中,将更名为 xx-node。例如 circle-node,rect-node,ellipse-node,star-node,image-node。
同理,边也将更名为 line-edge、polyline-edge、cubci-edge 等。
## 5️⃣. 功能引入
### v4 功能使用
v4 中所有功能都默认已经加入 G6,因此在 graph 配置时可以用字符串的方式指定,这导致了包体积庞大。例如:
```typescript
import { Graph } from '@antv/g6';
const graph = new Graph({
// ... 其他配置项
modes: {
default: ['drag-node', 'scroll-canvas'], // 交互名称
},
defaultNode: {
type: 'circle', // 节点类型名称
},
defaultEdge: {
type: 'rect', // 节点类型名称
},
layout: {
type: 'radial',
},
});
```
### v5 功能引入与使用
为了更好地支持 TreeShaking,v5 仅有部分最基础的能力会预先注册,其它已经实现的内置能力,但需要用户手动注册。同样地,自定义的能力也需要同样方式注册:
```typescript
import { Graph, extend, Extensions } from '@antv/g6';
// 外部引入的功能
import { ForceLayout as ForceLayoutWASM, supportsThreads, initThreads } from '@antv/layout-wasm';
// Class CustomBehaviorClass...
// Class CustomEdge...
const ExtGraph = extend(Graph, {
behaviors: {
'activate-relations': Extensions.ActivateRelations, // 内置的交互,未提前注册
'some-custom-behavior': CustomBehaviorClass, // 自定义交互
},
nodes: {
'modelRect-node': Extensions.ModelRectNode, // 内置的 modelRect 节点,未提前注册
},
edges: {
'custom-edge': CustomEdge, // 自定义边
},
layouts: {
'force-wasm': ForceLayoutWASM,
},
});
const supported = await supportsThreads();
const threads = await initThreads(supported);
// 使用 extend 后的图进行实例化
const graph = new ExtGraph({
// ... 其他配置项
modes: {
default: [
'drag-node', // 默认注册的交互
'activate-relations', // 刚刚引入并注册的内置交互
'some-custom-behavior', // 自定义并注册的交互
],
},
defaultNode: {
type: 'modelRect-node', // 刚刚引入并注册的内置节点类型
},
defaultEdge: {
type: 'custom-edge', // 自定义并注册的边类型
},
layout: {
type: 'force-wasm', // 刚刚从其他包引入并注册的布局算法
threads,
maxIteration: 200,
},
});
```
## 6️⃣. 布局使用
我们重构了 @antv/layout,考虑到包体积大小仅内置了 circular / concentric / grid / force 布局。在使用方式上和 v4 完全一致,通过 type 指定布局名称,传入其他布局参数:
```typescript
new Graph({
//...其他配置项
layout: {
type: 'force', // 布局名称
preventOverlap: true,
nodeSize: 30,
workerEnabled: true, // 支持在 WebWorker 中运行
},
});
```
对于非内置布局,我们提供了以下使用方式:
- @antv/layout 和 v4 保持一致的 JS 编写的串行布局算法;
- @antv/layout-wasm 提供基于 Rust 绑定到 WASM、多 WebWorker 并行的布局算法;
- @antv/layout-gpu 提供基于 WebGPU 的可并行布局算法;
- 用户完全自定义的布局。
相比 v4 多出了向 G6 运行时标准库注册布局这一步。另外,虽然由于实现不同有的需要额外的异步启动步骤,但是在 layout 的配置描述上均保持一致,即通过 type 指定布局名称,然后传入其他布局参数。
下面展示的是在 v5 中使用新增的 @antv/layout-wasm,首先需要向 G6 的运行时标准库注册,提供一个自定义布局名称,后续将它传给 `layout` 使用。
[WASM 布局 DEMO](https://g6-next.antv.antgroup.com/examples/feature/features/#wasmLayouts)
```typescript
import { stdLib, Graph } from '@antv/g6';
import { supportsThreads, initThreads, ForceLayout as ForceLayoutWASM } from '@antv/layout-wasm';
// 注册自定义布局
const ExtGraph = extend(Graph, {
layouts: {
'force-wasm': ForceLayoutWASM,
},
});
// 启动 WebWorker 线程池
const supported = await supportsThreads();
const threads = await initThreads(supported);
// 使用扩展后的 Graph
new ExtGraph({
//... 省略其他配置
layout: {
type: 'force-wasm', // 与注册时命名一致
threads, // 线程配置
dimensions: 2,
maxIteration: 100,
//... 省略该布局的其他参数
},
});
```
如果我们提供的布局实现都无法满足需求,还可以完全自定义布局。在实现 @antv/layout 提供的 Layout 接口时,只需要实现 execute 方法,assign 置空即可,这样可以保证不影响原始的图模型数据。
```javascript
import { Layout, LayoutMapping } from '@antv/layout';
class MyCustomLayout implements Layout<{}> {
async assign(graph, options?: {}): Promise